What’s the Difference Between HDPE and PET Plastics?
What is HDPE Plastic?
HDPE stands for high-density polyethylene. It is a highly durable, opaque petroleum-based thermoplastic that is resistant to heat, punctures, and impacts. A HDPE plastic is also resistant to corrosion and microbial growth.
How is HDPE made? By deriving ethane from ethylene gas. Then, the ethane is heated, mixed with benzene, and then exposed to UV radiation to catalyze the polymerization process. The polymer is poured into board-shaped molds and cooked at a low heat to eliminate any oxygen.
Once the boards are cooled, they will be shipped as raw materials that can be turned into a variety of products from plastic drums and shipping barrels to laundry detergent containers and facial prostheses.
HDPE has a melting point of 160°F which is higher than many other plastics making it exceptionally rigid and stable when cool. On the other hand, when heated above its melting point, it’s highly malleable.
What is PET Plastic?
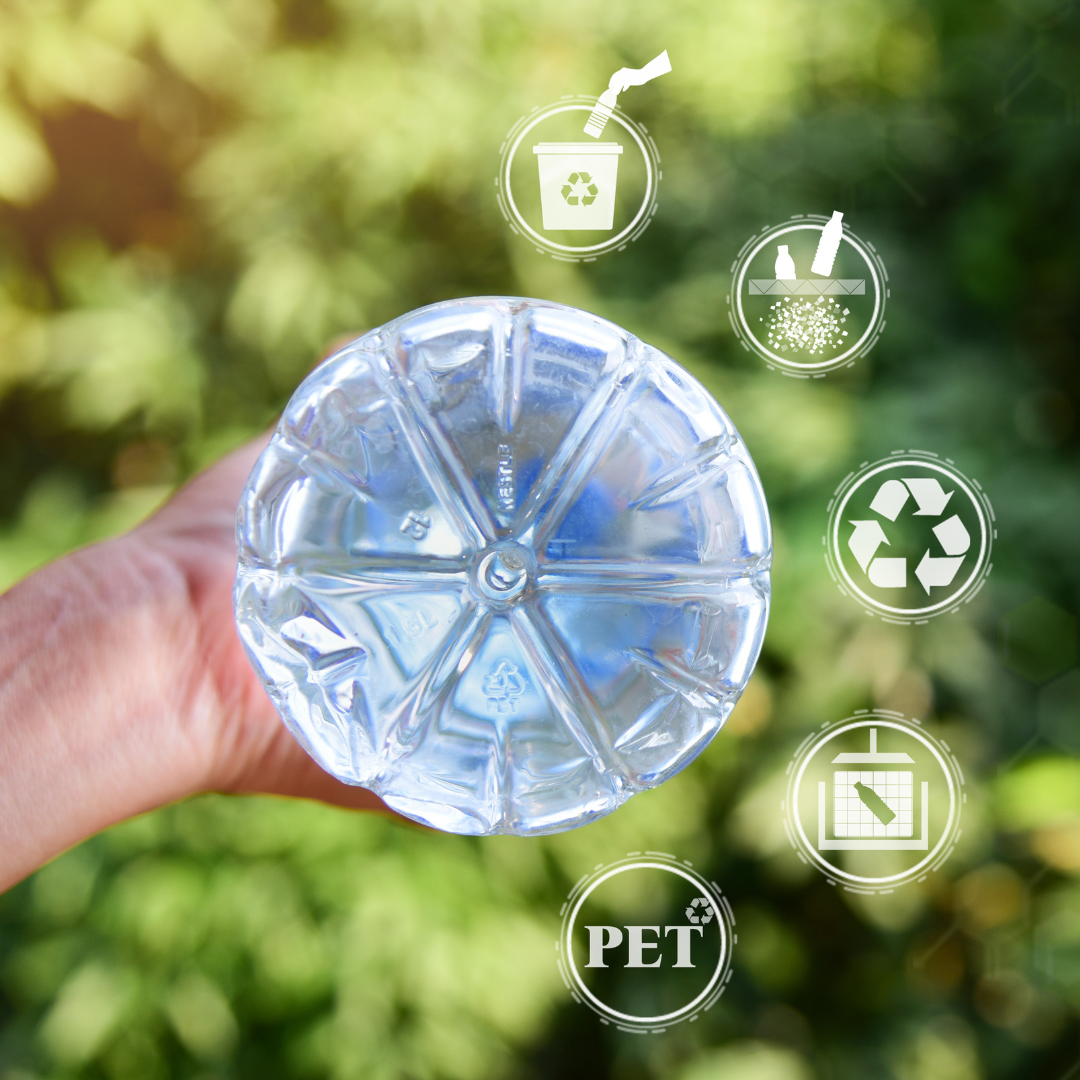
Polyethylene terephthalate, PET plastic, is a clear plastic that can withstand temperatures up to 145°F. Polyethylene terephthalate is the chemical name for polyester, and PET is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin in the polyester family. It is most commonly used in clothing fibers and containers for food and liquids.
How is PET plastic made? Ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid come together to form the polymer chain that results in the strands of PET that are then cut into small pellets, which will be heated and molded into the desired shape. PET plastics are FDA-approved for contact with food and beverages. They are also phthalate and BPA free.
PET plastics are a sustainable packaging option compared to aluminum or glass, though they are derived from natural gas and oils.
Key Differences Between PET and HPDE Plastics
HPDE and PET plastics are commonly used throughout the packaging and shipping industry, there are some notable differences that set them apart from each other.
Temperature Range
Both plastics are relatively heat-resistant, HPDE has a higher melting point than most at 160°F. HPDE plastics have a lower cold brittleness temperature than PET, resisting temperature up to -50°F while PET plastics can only handle temperatures as low as -40°F.
Stress Crack Resistance
Plastic materials go through environmental stress which creates cracking that can jeopardize the contents of the package. A stress crack is in external or internal crack cause by tensile stresses. Stress cracks happen frequently in HDPE plastics due to the chemicals in the environment that attack the semi-crystalline plastic material.
Crystallinity will decrease when the molecular weight of the plastic increases and improves resistance to environmental stress cracking.
*PET plastic containers have a higher resistance to stress cracking than HPDE plastics

Gas Barrier
A plastic’s gas barrier or WVTR (water vapor transmission rate) is measured in g-mil/100in 2/24hr, indicating the penetration of vaporized H2) through the plastic barrier. PET plastics have a WVTR of 2.0 2hile HDPE plastics have a WVTR of 0.5. When you have a lower WVTR that means the packaging type will protect its contents against moisture exposure for a longer period.
When needing to ship hazardous goods that require a hazmat box and accurate labeling, ensure your plastic packaging choice complies with the necessary WVTR for barrier performance.
Recyclability
Even though both PET and HDPE are recyclable plastics they need to be separated before recycling because they require different processes that breakdown their contents.
When you look at the base of each type of plastic, there will be a triangular label with a number inside of it. This number shows you the recycle rating. PET has a recycle rating of 1, while HDPE has a recycle rating of 2.
Plastics with a 1 rating are intended for a single use only, as heating and reusing these items can cause antimony to leech from the plastic. They are accepted by most U.S. jurisdictions and are easily recycled by shredding them into pallets.
Plastics with a 2 rating have a high strength-to-density ration meaning they are suitable for reuse and recycling. HDPE plastics can be recycled up to 10 times before disposal. Plastics with a 2 rating are often re-molded into pipes, lumber, toys, and floor tiles.